Spring 2016: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology (Geology 307)
Item set
- Title
- Spring 2016: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology (Geology 307)
Items
-
 This thin section contains some feldspar and quartz microphenocryst surrounded by a matrix of volcanic glass and some white needle-shaped microlites. Oikocryst is present, with feldspar inclusion. Many feldspars show oscillatory zoning and polysynthetic twinning, which suggests that the environment is not stable. Fiamme texture indicate that the original are formed when ignimbrites are emplaced at high temperature, and the lower portions typically become welded by the internal heat in the settled pile to a vary hard rock. They can usually be found in a pyroclastic flow deposit. Most of the crystal is euhedral or subhedral, and some crystal has a spherulitic texture. Therefore, this thin section might originate from a silicic pyroclastic flow deposit that cools quickly.
This thin section contains some feldspar and quartz microphenocryst surrounded by a matrix of volcanic glass and some white needle-shaped microlites. Oikocryst is present, with feldspar inclusion. Many feldspars show oscillatory zoning and polysynthetic twinning, which suggests that the environment is not stable. Fiamme texture indicate that the original are formed when ignimbrites are emplaced at high temperature, and the lower portions typically become welded by the internal heat in the settled pile to a vary hard rock. They can usually be found in a pyroclastic flow deposit. Most of the crystal is euhedral or subhedral, and some crystal has a spherulitic texture. Therefore, this thin section might originate from a silicic pyroclastic flow deposit that cools quickly. -
 This thin section contains feldspar phenocrysts surrounded by a matrix of feldspar and olivine microlite crystals. Many of the feldspars exhibit quality examples of twinning. Simple, tartain plaid, and Carlsbad twinning can be observed. The igneous textures indicate that the cooling process was initially slow, but cooled rapidly in an eruption to create this porphyritic texture. Throughout the sample there are areas full of volcanic glass with a holohyaline texture. The magma itself was not at equilibrium with the phenocrysts frozen inside, which can be seen through crystals with multiple embayments. An embayment occurs when the magma dissolves a phenocryst by corroding it from the outside faces into the inner parts of the crystal. Compositionally, the magma appears to be mafic, but has varying bands of minerals depending on the location within the thin section.
This thin section contains feldspar phenocrysts surrounded by a matrix of feldspar and olivine microlite crystals. Many of the feldspars exhibit quality examples of twinning. Simple, tartain plaid, and Carlsbad twinning can be observed. The igneous textures indicate that the cooling process was initially slow, but cooled rapidly in an eruption to create this porphyritic texture. Throughout the sample there are areas full of volcanic glass with a holohyaline texture. The magma itself was not at equilibrium with the phenocrysts frozen inside, which can be seen through crystals with multiple embayments. An embayment occurs when the magma dissolves a phenocryst by corroding it from the outside faces into the inner parts of the crystal. Compositionally, the magma appears to be mafic, but has varying bands of minerals depending on the location within the thin section. -
 Opaque, dull luster, dark brownish/metallic gray colored, extremely porous, igneous rock approximately 6cm in length. Scoria is mafic (generally basaltic) in nature with very small vesicles (
Opaque, dull luster, dark brownish/metallic gray colored, extremely porous, igneous rock approximately 6cm in length. Scoria is mafic (generally basaltic) in nature with very small vesicles ( -
 This is a rock with many parallel continuous distinct fine layers. There are mainly two colors of layers—black and white, so there may be two major compositions. The pattern is called flow banding. Flow banding is created in two ways. Mingling of two magmatic liquids in the magma chamber will create such pattern on the wall rock. Or when eruption happens, viscous lava can leave such pattern on the contact surface. Because lava usually cools quickly, the grain size of the rock is small.
This is a rock with many parallel continuous distinct fine layers. There are mainly two colors of layers—black and white, so there may be two major compositions. The pattern is called flow banding. Flow banding is created in two ways. Mingling of two magmatic liquids in the magma chamber will create such pattern on the wall rock. Or when eruption happens, viscous lava can leave such pattern on the contact surface. Because lava usually cools quickly, the grain size of the rock is small. -
 Volcanic ejecta approximately 18 cm long. Felsic in nature, and extremely porous. Impressions of gas bubbles are clearly visible.
Volcanic ejecta approximately 18 cm long. Felsic in nature, and extremely porous. Impressions of gas bubbles are clearly visible. -
 Pumice is a light colored, porous, igneous rock that forms during very explosive volcanic eruptions such as an eruption from a stratovolcano. Pumice differs from scoria by its smaller vesicles, thinner vesicle walls and being light colored and less dense. Vesicles are air bubbles that are trapped in the rock during the cooling process.
Pumice is a light colored, porous, igneous rock that forms during very explosive volcanic eruptions such as an eruption from a stratovolcano. Pumice differs from scoria by its smaller vesicles, thinner vesicle walls and being light colored and less dense. Vesicles are air bubbles that are trapped in the rock during the cooling process. -
 Chemical Formula: CaMgSi2O6 Compositional Family: calcium magnesium silicate Structural Family: Ca-clinopyroxene/single chain silicate Crystal System: monoclinic Location: Dekalb, St. Lawrence County, NY Texture: alone Crystal Form: single, short prismatic crystals with good terminations Color: greenish-gray, white, tannish Luster: vitreous/dull earthy Hardness: 5 to 6 Streak Color: white to light green Relative Density: medium (3.3-3.6) Transparency: translucent Cleavage/Fracture: 2 fair to good prismatic directions, meet at 87 and 93 degrees Common Associations: contact and regional metamorphic rocks
Chemical Formula: CaMgSi2O6 Compositional Family: calcium magnesium silicate Structural Family: Ca-clinopyroxene/single chain silicate Crystal System: monoclinic Location: Dekalb, St. Lawrence County, NY Texture: alone Crystal Form: single, short prismatic crystals with good terminations Color: greenish-gray, white, tannish Luster: vitreous/dull earthy Hardness: 5 to 6 Streak Color: white to light green Relative Density: medium (3.3-3.6) Transparency: translucent Cleavage/Fracture: 2 fair to good prismatic directions, meet at 87 and 93 degrees Common Associations: contact and regional metamorphic rocks -
 Chemical Formula: K(Mg,Fe2+)(Al,Fe3+)[(Al,Si)3O10](OH,F)2 Compositional Family: iron aluminum silicate Structural Family: sheet silicate/phyllosilicate Crystal System: monoclinic Location: Franklin, NJ Texture: in mass Crystal Form: micaceous mass Crystal Habit: elastic mica flakes/sheets Color: brown, black, brownish black Luster: vitreous/pearly Hardness: 2.5-3 Streak Color: white Relative Density: medium (2.8-3.4) Transparency: opaque Cleavage/Fracture: 1 perfect direction Common Associations: metamorphic rocks (schist, gneiss); igneous rocks (granite, rhyolite)
Chemical Formula: K(Mg,Fe2+)(Al,Fe3+)[(Al,Si)3O10](OH,F)2 Compositional Family: iron aluminum silicate Structural Family: sheet silicate/phyllosilicate Crystal System: monoclinic Location: Franklin, NJ Texture: in mass Crystal Form: micaceous mass Crystal Habit: elastic mica flakes/sheets Color: brown, black, brownish black Luster: vitreous/pearly Hardness: 2.5-3 Streak Color: white Relative Density: medium (2.8-3.4) Transparency: opaque Cleavage/Fracture: 1 perfect direction Common Associations: metamorphic rocks (schist, gneiss); igneous rocks (granite, rhyolite) -
 Characteristic quartz crystals emerging from solidified sediment. Layers of sediment are above and below crystals of quartz. 6-sided crystals are very clear. Vitreous luster with a deep brown/red color. This sample was found at Crystal Mountain, Colorado. The chemical formula is SiO2. Quartz is a framework silicate.
Characteristic quartz crystals emerging from solidified sediment. Layers of sediment are above and below crystals of quartz. 6-sided crystals are very clear. Vitreous luster with a deep brown/red color. This sample was found at Crystal Mountain, Colorado. The chemical formula is SiO2. Quartz is a framework silicate. -
 KAlSi3O8 (a feldspar). A pink, monoclinic, pearly crystal with 90o cleavage angle and uneven fracture. Commonly found in low temperature metamorphic rocks, as well as pegmatites and conglomerates.
KAlSi3O8 (a feldspar). A pink, monoclinic, pearly crystal with 90o cleavage angle and uneven fracture. Commonly found in low temperature metamorphic rocks, as well as pegmatites and conglomerates. -
 (Ca,Na)(Mg,Fe,Al)(Al,Si)2O6 (a pyroxene). Black, vitreous, monoclinic prism with cleavage at 87o and 93o. Commonly found in basalt, diabase, and gabbro, as well as with metamorphic serpentines. Dana 325. Specimen number S1567
(Ca,Na)(Mg,Fe,Al)(Al,Si)2O6 (a pyroxene). Black, vitreous, monoclinic prism with cleavage at 87o and 93o. Commonly found in basalt, diabase, and gabbro, as well as with metamorphic serpentines. Dana 325. Specimen number S1567 -
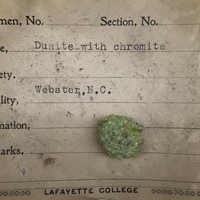 Collection: Lafayette College Student Collection Color: green Luster: vitreous Formula: (Mg, Fe)2SiO4 Hardness: 7 Fracture Habit: Massive
Collection: Lafayette College Student Collection Color: green Luster: vitreous Formula: (Mg, Fe)2SiO4 Hardness: 7 Fracture Habit: Massive -
 Collection: Lafayette College Student Collection Color: black Luster: vitreous Formula: K(Fe, Mg)3AlSi3O10(OH)2 Hardness: 2.5-3.0 Cleavage: one perfect Habit: Lamellar Typical Occurrence: Igneous rock, Metamorphic rock, Sedimentary rock
Collection: Lafayette College Student Collection Color: black Luster: vitreous Formula: K(Fe, Mg)3AlSi3O10(OH)2 Hardness: 2.5-3.0 Cleavage: one perfect Habit: Lamellar Typical Occurrence: Igneous rock, Metamorphic rock, Sedimentary rock -
 Collection: Lafayette College Location of origin: Virginia Name on collection tag: Amelia C.H. Formula: NaAlSi3O8 Hardness: 6- 6.5 Cleavage: perfect on {001}, very good on {010} Color: white to gray Luster: non-metallic, vitreous Habit: commonly tabular Crystal system: Triclinic Compositional family: plagioclase feldspar group Relative density: 2.6 - 2.65
Collection: Lafayette College Location of origin: Virginia Name on collection tag: Amelia C.H. Formula: NaAlSi3O8 Hardness: 6- 6.5 Cleavage: perfect on {001}, very good on {010} Color: white to gray Luster: non-metallic, vitreous Habit: commonly tabular Crystal system: Triclinic Compositional family: plagioclase feldspar group Relative density: 2.6 - 2.65 -
 Collection: Lafayette College Location of origin: Hot Springs, Arkansas Formula: SiO2 Structural group: Framework Silicate Hardness: 7 Cleavage: None, conchoidal fracture Color: colorless or gray Luster: non-metallic, vitreous Habit: has a vast range of habits Crystal system: Hexagonal Compositional family: Silicates (Silica group) Relative Density: 2.6-2.7
Collection: Lafayette College Location of origin: Hot Springs, Arkansas Formula: SiO2 Structural group: Framework Silicate Hardness: 7 Cleavage: None, conchoidal fracture Color: colorless or gray Luster: non-metallic, vitreous Habit: has a vast range of habits Crystal system: Hexagonal Compositional family: Silicates (Silica group) Relative Density: 2.6-2.7 -
 Lafayette College Mineral Collection Student Collection Mineral: orthoclase Sample number: 51258 Chemical formula: KAl〖Si〗_3 O_8 Color: brown / orange Luster: vitreous Hardness: 6 Cleavage: uneven fracture Compositional family: framework silicate Structural family: potassium feldspar group Crystal system: monoclinic Crystal habits: prismatic and tabular
Lafayette College Mineral Collection Student Collection Mineral: orthoclase Sample number: 51258 Chemical formula: KAl〖Si〗_3 O_8 Color: brown / orange Luster: vitreous Hardness: 6 Cleavage: uneven fracture Compositional family: framework silicate Structural family: potassium feldspar group Crystal system: monoclinic Crystal habits: prismatic and tabular
