Cross Section of a Mantle Plume
Item
-
Title
-
Cross Section of a Mantle Plume
-
Description
-
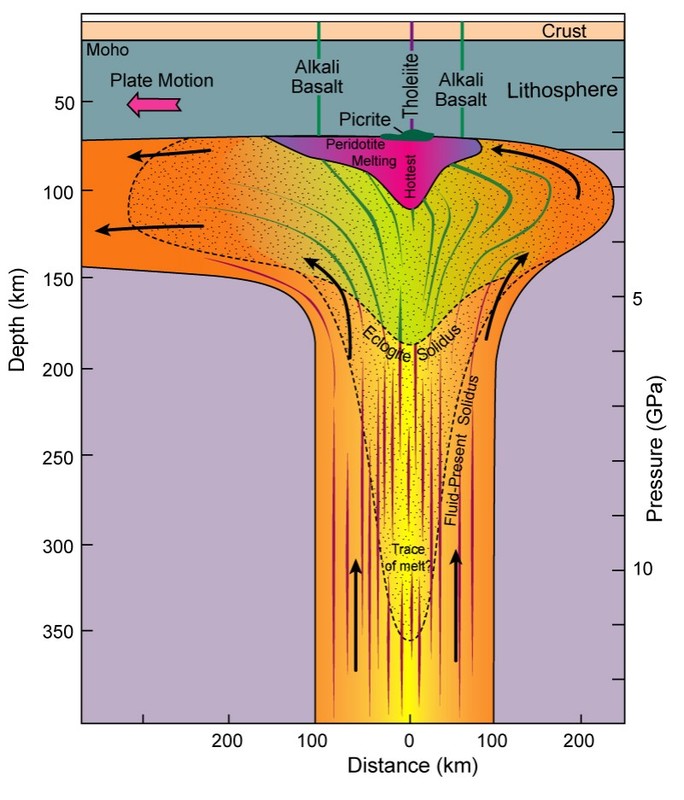
This cross-section of a mantle plume is representative of the offshoots of the superplume that created the Austral-Cook Islands. Mantle plumes originate as masses of heat and solid rock from the core-mantle boundary, potentially as the result of a subducted plate reaching the D' Layer. At shallower depths, they begin to melt in three phases, as shown on the diagram. The edges of the plume are more alkaline than the tholeiitic interior. This difference is due to the extent of melting on the edge of the plume, which is cooler due to heat loss with the surrounding country rock versus the hot interior of the plume. Because there is a lower melt fraction at the edges of the plume, it tends to be richer in incompatible elements, which are quick to escape from a melt.
-
Subject
-
Petrology 2015 Final Project: OIB
-
Creator
-
Devon Gorbey
-
Source
-
John D. Winter, "Principles of Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology"
-
Mediator
-
Tamara Carley