Compare and Contrast of Asterdam and the Saint Paul Islands with the Canary Islands
Item
-
Title
-
Compare and Contrast of Asterdam and the Saint Paul Islands with the Canary Islands
-
Description
-
A comparative look at the landforms, magma settings, and the geochemistry of two ocean island chains.
-
Amsterdam and St. Paul
Hotspot magmatism with ridge influence for magma generation
Volcanic Island chain-- Amsterdam & St. Paul separated by transform fault
Mixture of Alkaline and Tholeiitic Rocks
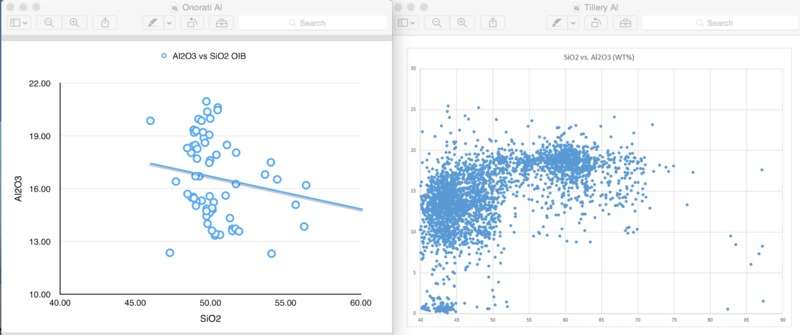
Some samples found low in alumina compared to Canary islands
caused by ridge influence
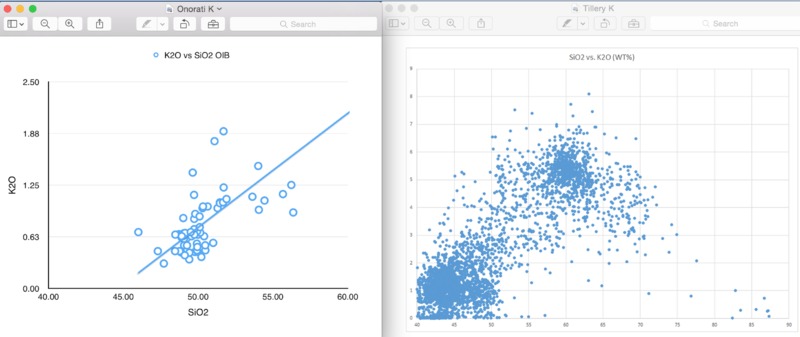
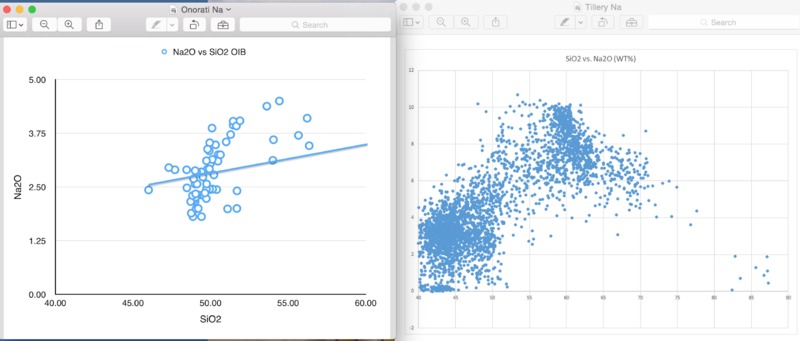
Al, Na, K behave incompatibly
Al weight percentages similar between Amsterdam and Canary Islands
Lower weight percentage of K than Canary islands due to ridge influence
Lower weight percentage of Na than Canary islands due to ridge influence
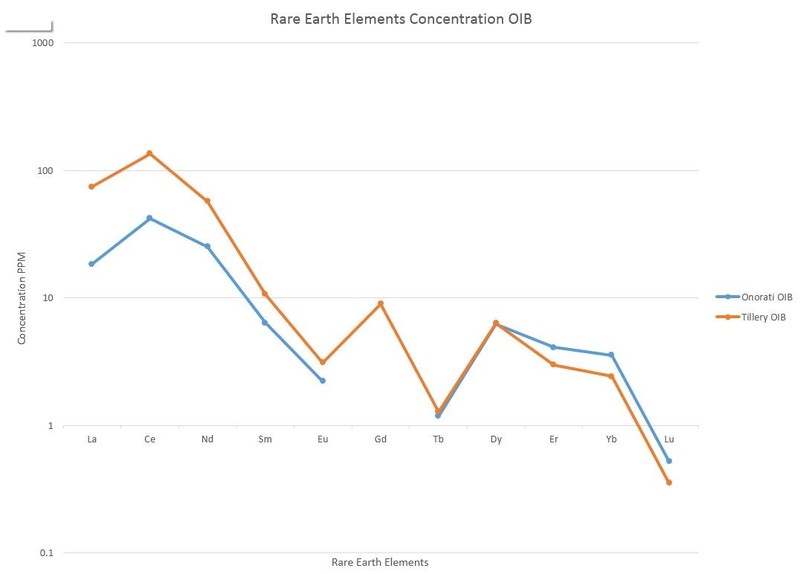
REE slope trends similar, concentration difference due to ridge influence diluting REE concentration. Direct magmatism from hotspot plume on Canary islands keep mantle-like concentrations.
-Mostly shield volcanos
Antarctic Plate moving southward at 1cm. per year.
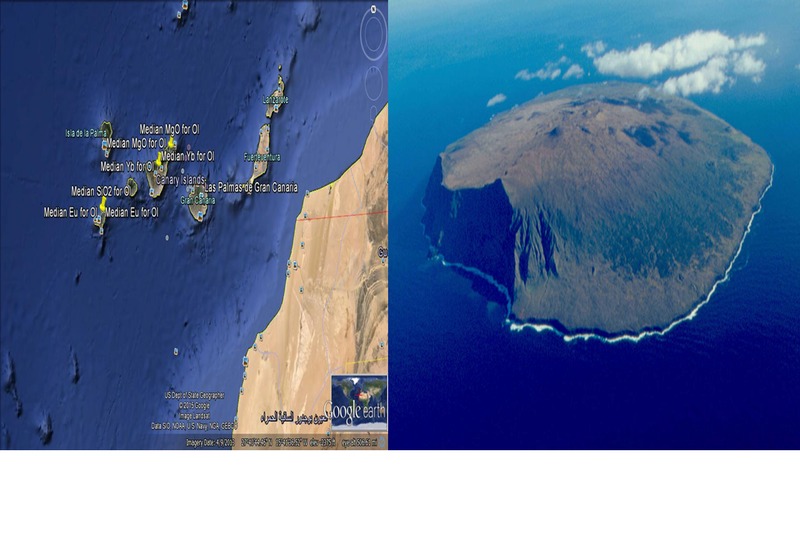
The Canary Islands
Intraplate island arc on a passive margin (Hotspot)
Generation of magma due to hotspot (adiabatic rising solid heated rock)
Volcanic Island chain with a Seamount Chain
Mixture of Alkaline and Tholeiitic Rocks
Al, Na, K, and REEs behave incompatibly
Eu strange exception, behaves more compatibly than lathanides directly next to it
Relatively high levels of K compared to Amsterdam and St. Paul Islands
Relatively high levels of Al compared to Amsterdam and St. Paul Islands
Discrepancies likely a result of a lack of ridge influence on the Canary Islands
Mostly Shield Volcanoes
Younger to Southwest, older to Northeast
African plate moving 2.5 cm/a to the Northeast
 https://exhibits.lafayette.edu/geology/files/original/b8f2c724ccc9a43a4b6f68d087cc8e95.png
https://exhibits.lafayette.edu/geology/files/original/b8f2c724ccc9a43a4b6f68d087cc8e95.png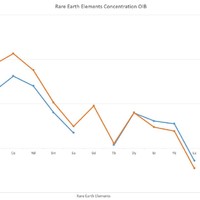 https://exhibits.lafayette.edu/geology/files/original/e66aa28e9a7dd8f8c3e1d96ea22a9694.jpg
https://exhibits.lafayette.edu/geology/files/original/e66aa28e9a7dd8f8c3e1d96ea22a9694.jpg https://exhibits.lafayette.edu/geology/files/original/bdd5a7e08931777eebad4a7e1eb7509b.png
https://exhibits.lafayette.edu/geology/files/original/bdd5a7e08931777eebad4a7e1eb7509b.png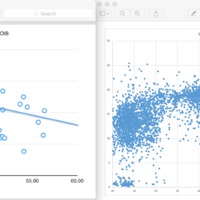 https://exhibits.lafayette.edu/geology/files/original/ad202328fb059da0fa20743ca4a3e614.png
https://exhibits.lafayette.edu/geology/files/original/ad202328fb059da0fa20743ca4a3e614.png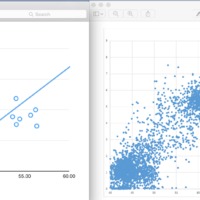 https://exhibits.lafayette.edu/geology/files/original/5a21b105dff81dbb9f4905dcd7976f14.png
https://exhibits.lafayette.edu/geology/files/original/5a21b105dff81dbb9f4905dcd7976f14.png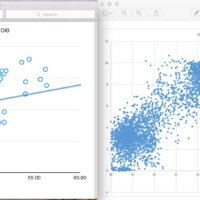 https://exhibits.lafayette.edu/geology/files/original/44dd4521c0aa1664c99933b9dca61af7.png
https://exhibits.lafayette.edu/geology/files/original/44dd4521c0aa1664c99933b9dca61af7.png